History
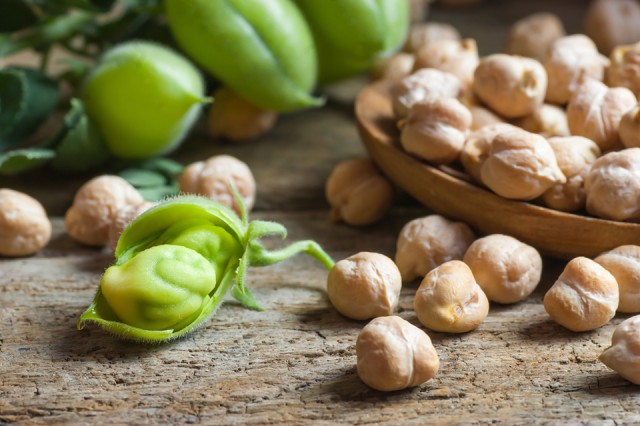
Chickpeas are the seed of the annual plant Cicer arietinum of the pea (Fabaceae, or leguminosae) family, widely grown for its nutritious seeds. The oldest records of the cultivated chickpea are from Türkiye, where it was grown approximately 7,500 years ago. From there, the crop spread and became a staple food across the Middle East, North Africa and the Indian subcontinent. Today, chickpeas are popular throughout China, India, North and Eastern Africa, Europe, the Americas and Australia. Chickpeas are consumed fresh as a green vegetable, parched, fried, roasted and boiled. They are also consumed as a snack food, sweets and condiments or as a paste such as hummus. They are also ground into flour and used to make soup, bread and sweetmeats.

Healthy Diet
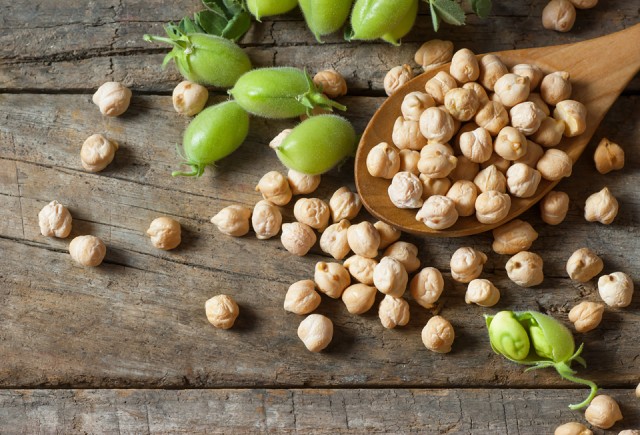
Chickpeas consumption can assist in the treatment of diabetes and high cholesterol. Chickpeas contain 13 percent protein, 40 percent to 55 percent carbohydrate, and 4 to 10 percent oil. Fatty acid composition varies with chickpea type, but is approximately 50 percent oleic and 40 percent linoleic oils. Chickpeas are also an excellent source of folate, vitamins B6 and C, and zinc.